Vitamin E Polyethylene Glycol Succinate
( NMPA CDE NO.: F20240000529)
Name: Vitamin E Polyethylene Glycol Succinate
Other Name: Vitamin E TPGS
M.F.: (C2H4O)nC33H54O5 n=20-22
M.W.: ≈1513
CAS No.: 9002-96-4
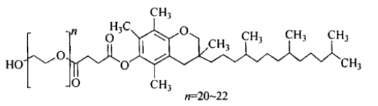
Quality Standard: USP; ChP.
Category: Nonionic surfactant; Solubilizer; Emulsifier
Melting Point: 39℃
Appearance: White to pale yellow waxy solid. Free soluble in water, most polar organic solvents such as ethanol.
Liquid crystalline phase:The mass fraction of solubility in water at room temperature is 20%. If the concentration exceeds this value, a high-viscosity liquid crystal phase will form. As the concentration in water increases, the structure of the liquid crystal phase gradually changes, from isotropic spherical micelles to cylindrical micelles, regular hexagonal micelles, reverse spherical micelles, and finally to a thin-layer lamellar liquid crystal state.
Stability:It has a relatively high degradation temperature, remains stable at 200℃, is stable in the air, but becomes unstable when exposed to alkali.
Critical micelle concentration (CMC): 0.02%(25℃)
HLB: About 13-17
Application:
1.Surface activity effect / Improving drug absorption and enhancing bioavailability
Due to its amphiphilic nature and good water solubility, TPGS is an excellent non-ionic surfactant for lipophilic substances. When it forms micelles or emulsions with poorly soluble drugs, it significantly enhances the absorption of the drugs in the gastrointestinal tract. TPGS has a structure similar to tocopherol esters, thus having certain antioxidant properties, which help to increase the stability of the formulation. TPGS has an inhibitory effect on P-glycoprotein, and when drugs that are transported through P-glycoprotein inhibition (such as doxorubicin, paclitaxel, vindesine, etc.) are combined with TPGS, their absorption in the gastrointestinal tract is significantly increased.
2.Carriers for water-insoluble or lipid-soluble drug delivery systems
By reacting the carboxyl groups in the TPGS molecule with the insoluble drugs, TPGS polymers – drug conjugates can be synthesized. After the composite nano-carriers are transported to the target site, they undergo metabolism in the body, and the drugs are released from the carriers to achieve targeted drug delivery.
3.Natural nutrient supplementation / Safety and efficacy of water-soluble vitamin E
Vitamin E TPGS is also used as an effective source of natural vitamin E for therapeutic and nutritional purposes. TPGS is a water-soluble vitamin E, which, unlike fat-soluble vitamin E, is absorbed by the body through a completely different mechanism. Fat-soluble vitamin E requires the assistance of bile salts in the intestinal cavity to be absorbed into the intestinal cells, while TPGS can transport vitamin E into intestinal cells by itself without the need for bile salt intervention.
| Application | Function | Example |
| Oral solution | Solubilizer, absorption enhancer | AGENERASE® Oral solution |
